1.2 Ultrastructure of cells
Eukaryotes
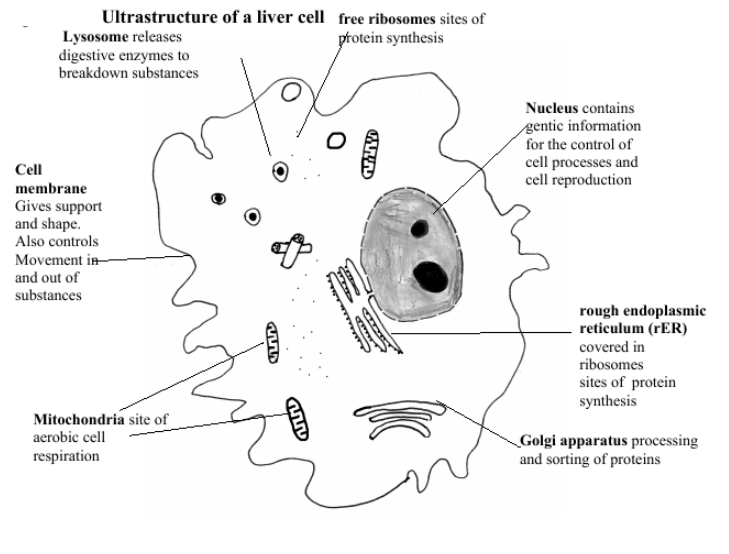 Figure 1.2.3
Figure 1.2.3
|
A table to compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
|
|
|
Prokaryotic cells |
Eukaryotic cells |
|
Have naked DNA The DNA is in cytoplasm They have no mitochondria The ribosomes are 70S that means smaller No membrane bound structures |
DNA is associated with proteins DNA is enclosed in a nuclear envelope They have mitochondria The ribosomes are 80S that means larger have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions. |
Similarity and Diversity of cells as evidence for their evolution
The plant and animal kingdom (as well as Fungi and Protists) contain living organisms made of eukaryotic cells. This means that the main structures are usually very similar. Biologists believe this is good evidence for the idea that all this diversity evolved from common ancestor cells. As the populations of cells have become adapted to their environments, differences have developed.
However there are some major differences between plant and animal cells.
Animal cells have no cell wall or chloroplasts and only have small vacuoles whereas plant cells have a large central vacuole.
