1.1 Introduction to cells
Surface area to volume ratio as a factor limiting cell size
Cells perform many functions and activities inside their structure. This is known as their metabolism. These activities often need a supply of substances such as oxygen or nutrients such as glucose. Cells also produce waste substances such as Carbon dioxide and they also produce heat from respiration. The amount of these substances and heat depend on how large the volume of the cell is. If the volume doubles then the demand for these substances will also double.
The needs of a cell depend on its volume.
Cells need to transport these substances and heat into and out of there surface membranes.
The ability to meet these transport needs depends on its surface area.
If we look at the mathematics of surface and volume we see that as a cell grows the relationship between surface area and volume gets smaller.
Imagine we had a cell that has a edge size of 1 μm. It would have a volume of 1 μm3 and each face would have an area of 1 μm2 making a total surface area of 6 μm2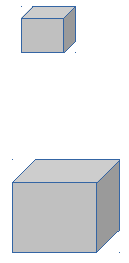 .
.
The ratio of surface area to volume would then be 6.
Then if the cell doubled its length to 2 μm It would have a volume of 8 μm3 and each face would have an area of 4 μm2 making a total surface area of 24 μm2 .
The ratio of surface area to volume would then be 3.
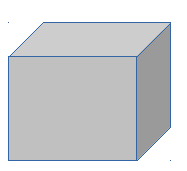
Then if the cell trebled its length to 3 μm It would have a volume of 27 μm3 and each face would have an area of 9 μm2 making a total surface area of 54 μm2 .
The ratio of surface area to volume would then be 2.
So the cell if it was three times as large would need 27 times the amount of substances and heat to be transported but only 9 times as much surface to be able to do this. The large cell, instead of 6 units of surface supplying for every unit of volume as in the small cell it would only have 2 units of surface supplying every unit of volume. This means it could not easily perform its living functions. This is why cells are generally very small.
