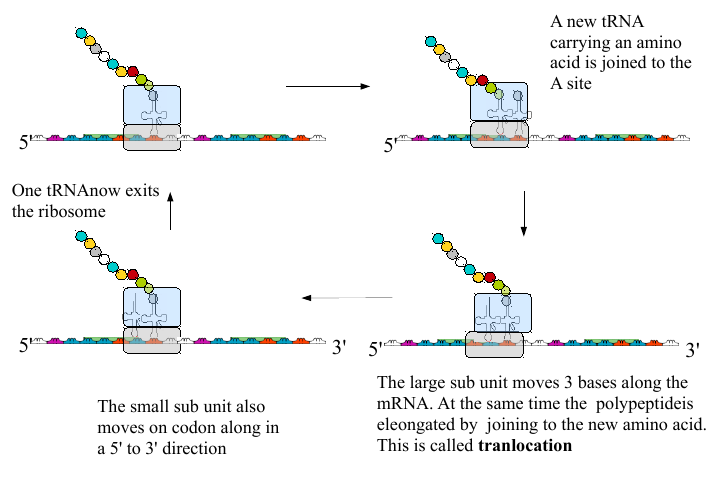
Elongation
The polypeptide is formed by many repeats of this cycle of events. Each cycle adds one amino acid to the polypeptide.
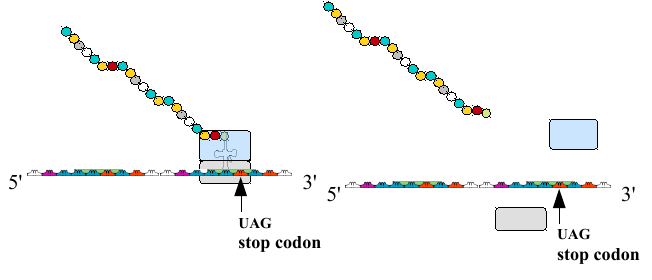
Termination
The cycle of elongation continues many times until the A site reaches what is called a stop codon.
No tRNA can bind to this. A special releasing factor joins instead and then the polypeptide is released and the ribosome splits apart into the small and large subunits.